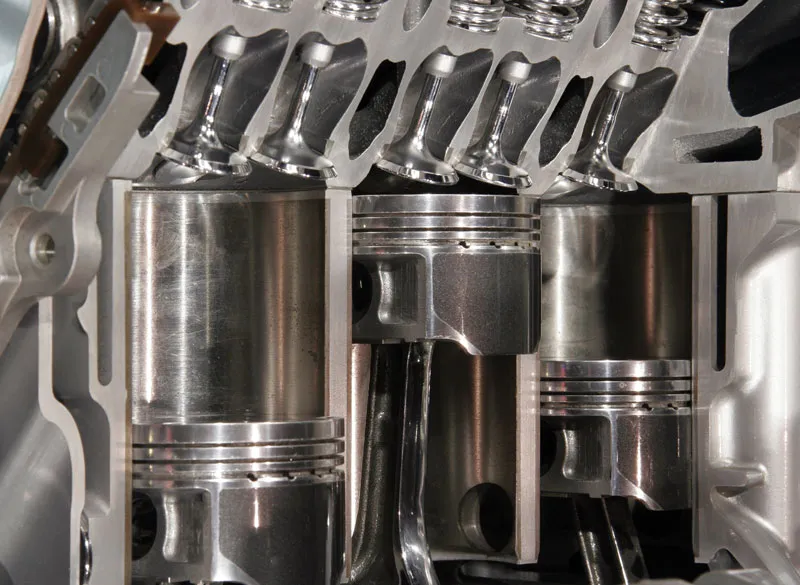
When it comes to internal combustion engines, few components are more critical than the piston and cylinder. They work together in a tightly coordinated dance to convert fuel into the mechanical power that drives your vehicle. Whether you’re a curious driver or a budding mechanic, understanding the function, design, and importance of pistons and cylinders is key to appreciating how engines work.
In this article, we’ll explore what pistons and cylinders are, how they work together, common problems, and how to keep them performing at their best.
🔧 What Is a Piston?
A piston is a cylindrical metal component that moves up and down inside the engine’s cylinder. It plays a vital role in the combustion process by compressing the air-fuel mixture and transmitting the force of the explosion to the crankshaft via the connecting rod.
✅ Key Functions of the Piston:
- Compresses the air-fuel mixture
- Transfers combustion force to the crankshaft
- Helps seal the combustion chamber
- Assists with oil control through piston rings
🏗️ What Is a Cylinder?
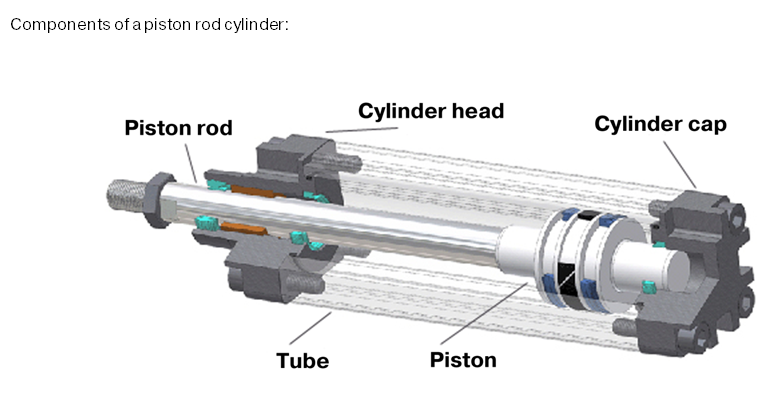
A cylinder is a hollow tube in the engine block in which the piston moves. It forms the combustion chamber where fuel is burned to produce power. Most modern engines have 3 to 8 cylinders, depending on their size and purpose.
✅ Key Functions of the Cylinder:
- Guides piston movement
- Houses the combustion chamber
- Transfers heat from combustion to the cooling system
🔁 How the Piston and Cylinder Work Together
The piston and cylinder form the core of the internal combustion process. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how they work together in a 4-stroke engine:
1. Intake Stroke
The piston moves downward, drawing in an air-fuel mixture through the intake valve.
2. Compression Stroke
The piston moves back up, compressing the mixture into a small space for efficient combustion.
3. Power Stroke (Combustion)
The spark plug ignites the mixture, causing a mini explosion that pushes the piston downward with force.
4. Exhaust Stroke
The piston moves up again, pushing exhaust gases out of the cylinder through the exhaust valve.
This cycle repeats rapidly—often thousands of times per minute—to produce continuous power.
⚙️ Piston Components and Design
A modern piston consists of several key parts:
- Piston Crown – The top surface that faces combustion
- Piston Skirt – The lower section that guides movement in the cylinder
- Piston Rings – Metal rings that seal the combustion chamber and control oil
- Piston Pin (Gudgeon Pin) – Connects the piston to the connecting rod
Most pistons are made from aluminum alloy due to its light weight and excellent heat conductivity.
⚠️ Common Piston and Cylinder Problems
1. Piston Slap
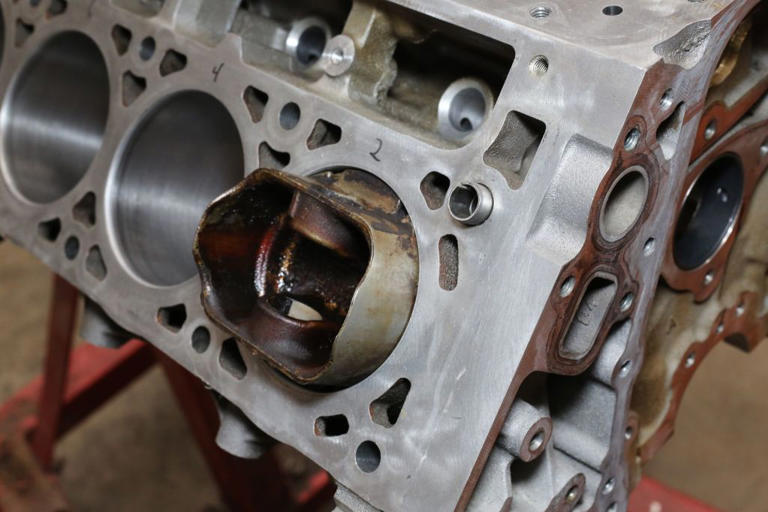

A knocking noise caused by the piston rocking side to side in a worn cylinder bore.
2. Worn Piston Rings
Leads to low compression, oil burning, and loss of power.
3. Cylinder Scoring
Scratches on the cylinder wall that can result from poor lubrication or foreign debris.
4. Cracked Pistons
Usually caused by engine knock, overheating, or detonation.
5. Stuck or Broken Rings
Can cause oil leaks, smoke from the exhaust, and poor engine performance.
🧰 Tips to Maintain Piston and Cylinder Health
- 🛢️ Use high-quality engine oil and change it regularly
- 🚫 Avoid engine overheating
- 🧼 Keep the air intake system clean to prevent debris from entering the cylinders
- 🔧 Address knocking or detonation early
- 🚗 Allow your engine to warm up before heavy acceleration
📊 Piston and Cylinder in Performance Engines
In performance or racing engines:
- Forged pistons are used for added strength
- Oversized cylinders increase engine displacement and power
- High-compression pistons improve efficiency and performance
- Cylinder liners or sleeves allow for easier rebuilds and repairs
FAQs About Pistons and Cylinders
Q1: How many pistons does my engine have?
It depends on the engine type. A 4-cylinder engine has 4 pistons, a V6 has 6, and so on.
Q2: What causes a piston to fail?
Common causes include overheating, poor lubrication, detonation, and manufacturing defects.
Q3: Can you replace just one piston?
Yes, but it’s best to inspect and balance all pistons during a rebuild to ensure performance and reliability.
Q4: What is the difference between a piston and a cylinder?
The piston is a moving part that travels up and down; the cylinder is the fixed chamber it moves within.
Q5: How do I know if my piston rings are bad?
Signs include excessive oil consumption, blue smoke from the exhaust, and loss of engine power.
Q6: Do diesel engines use pistons and cylinders too?
Yes. The basic piston-cylinder design applies to both gasoline and diesel engines, although diesel pistons are often stronger.
Q7: What materials are pistons made from?
Most are made from aluminum alloy; performance engines may use forged aluminum or steel.
Q8: Can a damaged cylinder be repaired?
In many cases, yes. Mechanics can bore out the cylinder and install an oversized piston or a cylinder sleeve.
Conclusion: Pistons and Cylinders – Power at the Core
The piston and cylinder are at the very heart of your engine’s operation. Working in perfect harmony, they convert fuel into power that moves your vehicle. Understanding their function, common problems, and how to maintain them is essential for any car owner who wants a reliable, efficient engine. Regular maintenance, high-quality fuel and oil, and paying attention to early warning signs will help keep your pistons and cylinders running strong for years to come.




