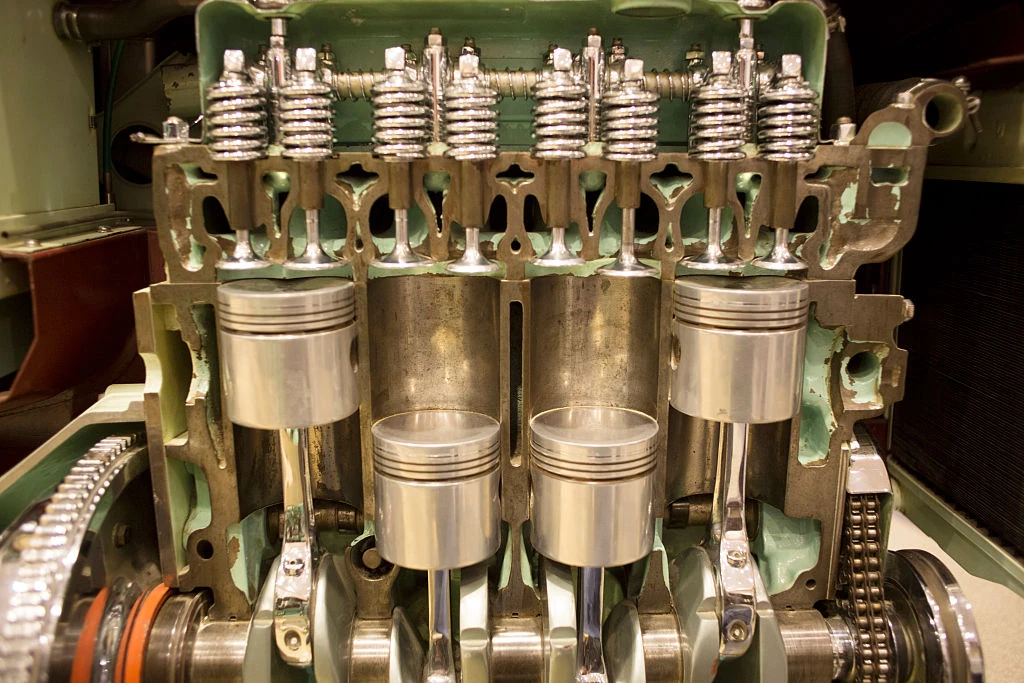
The internal combustion engine (ICE) is one of the greatest innovations in the history of mechanical engineering. From powering cars and motorcycles to running airplanes and generators, ICEs have been the backbone of transportation and industry for over a century.
This in-depth guide will help you understand everything you need to know about internal combustion engines — including how they work, their key components, different types, benefits, limitations, and the future of engine technology.
🧠 What is an Internal Combustion Engine?
An internal combustion engine is a mechanical device that converts the chemical energy of fuel (such as petrol, diesel, or gas) into mechanical energy through a process called combustion. The combustion takes place internally, within the engine’s cylinders, which is why it’s called an “internal” combustion engine.
This powerful device is widely used in:
- Automobiles
- Motorcycles
- Ships
- Airplanes
- Generators
- Industrial machines
⚙️ How Does an Internal Combustion Engine Work?
An ICE works on the principle of controlled explosions. Here’s a breakdown of the four-stroke cycle, which is the most common type:
1. Intake Stroke
The intake valve opens, and a mixture of fuel and air is drawn into the combustion chamber as the piston moves down.
2. Compression Stroke
The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the fuel-air mixture into a high-pressure state.
3. Power Stroke
A spark plug ignites the compressed fuel-air mixture, causing an explosion. The expanding gases force the piston downward — this is where energy is generated.
4. Exhaust Stroke
The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves up again to expel the burnt gases out of the chamber.
This four-stroke cycle repeats thousands of times per minute, generating the continuous power that drives vehicles.
🔧 Main Components of an Internal Combustion Engine
To understand ICEs better, let’s look at the key components involved in its functioning:
- Cylinder Block: The main body that houses cylinders.
- Pistons: Move up and down to compress and transfer energy.
- Crankshaft: Converts the piston’s motion into rotational energy.
- Camshaft: Opens and closes the intake and exhaust valves.
- Spark Plug: Ignites the air-fuel mixture (in petrol engines).
- Fuel Injector: Sprays fuel into the combustion chamber.
- Valves: Control air and exhaust flow in and out of the cylinder.
- Cooling System: Prevents the engine from overheating.
- Lubrication System: Ensures smooth movement of engine parts.
🔄 Types of Internal Combustion Engines
ICEs are classified based on several factors like the type of fuel, number of strokes, and arrangement of cylinders. Here are the most common types:
🔹 1. Based on Fuel Type
- Petrol (Gasoline) Engine
Uses spark ignition; smoother and quieter; found in most cars. - Diesel Engine
Uses compression ignition; more fuel-efficient; common in trucks and buses. - Gas Engines
Use LPG or CNG; used in taxis, rickshaws, and eco-friendly vehicles.
🔹 2. Based on Operation Cycle
- Two-Stroke Engine
Completes a power cycle in two strokes. Simpler, lighter, but less efficient. - Four-Stroke Engine
Most common type. Completes cycle in four strokes, offering better efficiency and performance.
🔹 3. Based on Cylinder Arrangement
- Inline Engine
Cylinders arranged in a straight line; compact and simple. - V-Type Engine
Cylinders arranged in a V shape; offers more power in less space. - Boxer Engine
Opposing cylinders; used in performance cars and aircraft.
✅ Advantages of Internal Combustion Engines
- High Power Output: Can produce large amounts of torque and horsepower.
- Compact & Lightweight: Easier to install in vehicles and machines.
- Quick Startup: Instant ignition and fast power generation.
- Readily Available Fuel: Petrol and diesel are globally accessible.
- Cost-Effective: Mass production and mature technology make them affordable.
- Versatile: Used across industries — from transport to agriculture.
❌ Disadvantages of Internal Combustion Engines
- Pollution: Emits CO₂, NOx, and other harmful gases.
- Fuel Dependency: Relies on non-renewable fossil fuels.
- Noise & Vibration: Can be noisy, especially in diesel variants.
- Maintenance: Requires regular oil changes, part replacements, and servicing.
🌱 The Future of Internal Combustion Engines

With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and the push for clean energy, internal combustion engines are undergoing a transformation. Companies are developing:
- Hybrid Engines (ICE + Electric motor)
- Hydrogen Fuel Engines
- Low-emission ICEs with cleaner combustion
- Biofuel-compatible engines
Although EVs are growing fast, ICEs are still dominant, especially in developing countries where fuel infrastructure and cost play a major role.
FAQ’s
1. What is the difference between an internal and external combustion engine?
An internal combustion engine burns fuel inside the engine’s cylinders, while an external combustion engine (like a steam engine) burns fuel outside and transfers heat through a medium like water.
2. Why are internal combustion engines still widely used?
ICEs are compact, powerful, affordable, and have a vast fuel infrastructure globally. These factors make them ideal for cars, trucks, and industrial machinery even today.
3. How does a spark plug work in a petrol engine?
The spark plug generates a small electric spark that ignites the compressed fuel-air mixture inside the cylinder, starting the combustion process that powers the engine.
4. What causes an engine to overheat?
Overheating can result from low coolant levels, a faulty radiator, a stuck thermostat, or a broken water pump, all of which affect the engine’s cooling system.
5. Can internal combustion engines run on alternative fuels?
Yes, many ICEs can be modified or built to run on alternative fuels like ethanol, biodiesel, LPG, or even hydrogen to reduce emissions.
6. What are the main components of an internal combustion engine?
Key components include the cylinder, piston, crankshaft, camshaft, spark plug (in petrol engines), valves, and the fuel injection system.
7. Are diesel engines more efficient than petrol engines?
Generally, yes. Diesel engines offer better fuel efficiency and more torque, making them ideal for heavy vehicles and long-distance travel.
8. What is the future of internal combustion engines in a world shifting to electric vehicles?
While electric vehicles are gaining popularity, ICEs are still being improved with cleaner technologies, hybrid systems, and compatibility with biofuels for a more sustainable future.
Final Thoughts
The internal combustion engine has shaped the modern world by making transportation faster, industries more productive, and life more mobile. While electric and sustainable alternatives are emerging, ICE technology is still evolving and adapting to meet modern environmental standards. Understanding how these engines work and their role in our daily lives helps us appreciate their value — even as we shift toward a cleaner, more efficient future.